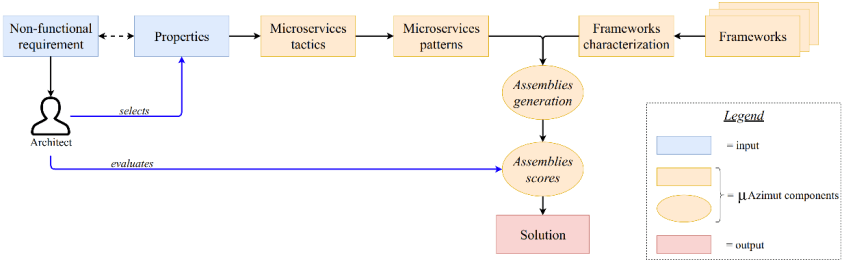
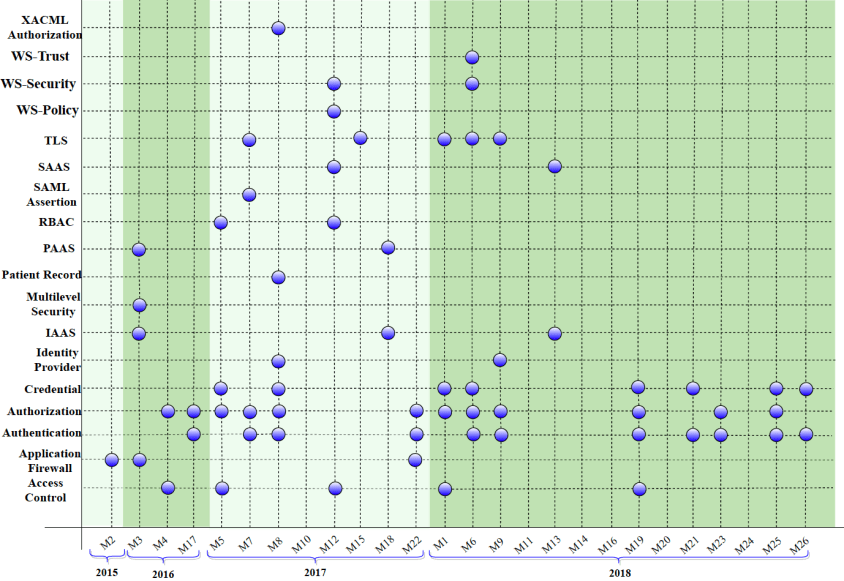
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) are real-time, patient-centered records that instantly and securely make information available to authorized users. The information contained in EHRs is sensitive since, in general, it consists of the patient’s medical history (hospitalizations, treatments, illnesses, among others).
One of the most relevant aspects of EHRs is security. More specifically, Confidentiality and Privacy are critical attributes for security in EHRs. In this regard, assessing the security of EHRs (and systems, in general) is too complex. Security can be characterized from institutional policies to sophisticated attacks on software and critical infrastructure. Therefore, to help reduce this complexity, we are working on a quality model to evaluate the current state of EHR security to support security decision-making in software vendors and clinical facilities. The first version of this quality model was evaluated with 20 professionals from the Chilean healthcare industry.

We are improving the model and, at the same time, developing a platform that will allow us to automate this evaluation.